'The cycle has been broken:' Manitoba First Nation signs child welfare agreement
Peguis First Nation celebrated a historic moment Tuesday as it became the first Indigenous community in Manitoba to take control of child welfare under federal legislation that came into effect three years ago.
The First Nation was joined by federal Indigenous Services Minister Patty Hajdu, Manitoba Premier Heather Stefanson and Manitoba Families Minister Rochelle Squires in the signing of a co-ordination agreement between the three governments.
"The cycle has been broken now. It's our care that is going to be provided, and that is something that we haven't had in a long time," Peguis First Nation Chief Glenn Hudson said after the ceremony.
The First Nation is one of just over two dozen communities that have notified Indigenous Services Canada that they intend to handle their own child and family services as outlined in the federal Act Respecting First Nations, Inuit and Metis Children, Youth and Families.
Elders and knowledge keepers sat on rugs made out of bison fur in the middle of the room. Ceremonial tools were used to conduct a pipe and water ceremony to start off the day.
The community requested the agreement in 2021. Under the federal legislation, the First Nation's own law came into effect one year ago, but the province did not sign on at the time.
This is the first time Manitoba has signed such an agreement, after it previously expressed concerns about the legislation.
"I know this process wasn't quick, but we are here now. The very first in Manitoba to undertake legislation and honour our children and families," said Hudson. "It's long overdue."
Under Peguis First Nation's law, its members across the country will have access to prevention services. The legislation has a focus on prevention so families can receive support to remain together.
Peguis will assume jurisdiction of intake services, child abuse investigations, after-hours services and early intervention services for members who reside off and on reserve. As part of the agreement, if another agency becomes involved with a child, youth or family from the community, it must notify Peguis Child and Family Services.
The agreement includes a three-year, $319-million commitment from the federal government to fund all aspects of child and family services.
"It's expensive to keep families together, but what's more expensive are families that fall apart," said Hajdu.
"This is actually the prevention that communities across the country need to keep families intact. That's how we're going to turn the tables on some of those significant struggles that communities are facing across the country."
Indigenous children and youth are vastly overrepresented in the child welfare system in Manitoba and across the country.
Some have called the current system the "Millennium Scoop" in reference to the '60s Scoop, the practice of removing Indigenous children from their parents at birth.
Interactions with the child welfare system have been linked to the high number of Indigenous people who have been involved with the justice system, addictions, mental health issues and homelessness.
Hudson said gaining control means children who end up getting involved with the system will still have access to their culture and their community while their parents get support.
Peguis has seen success since its law came into effect last year. At that time, there were more than 250 members in care, and since then about 100 of them have been transferred back to the First Nation, said Clemene Hornbrook, executive director of Peguis Child and Family Services.
She added the agency has prevented about 60 children from entering care.
"We are not taking our families or our children to court. We are sitting with our elders and we are implementing our traditional ways and practices as we deliver services to our members," said Hornbrook.
The province said it will still provide money allotted to Peguis before the agreement was signed. Manitoba is also working with several other Indigenous groups that are exercising their jurisdiction.
"We're really looking forward to working with them as a province to ensure that the child welfare system is truly transformed," said Squires.
Cowessess First Nation in Saskatchewan was the first group in Canada to take over child welfare in July 2021.
Peguis is the third Indigenous group to sign a co-ordination agreement with provincial and federal governments.
"We work at the speed of First Nations. This is not a colonial imposition of a new system. This is about providing the sufficient resources so that First Nations can take back that authority," said Hajdu.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Jan. 31, 2023.
CTVNews.ca Top Stories
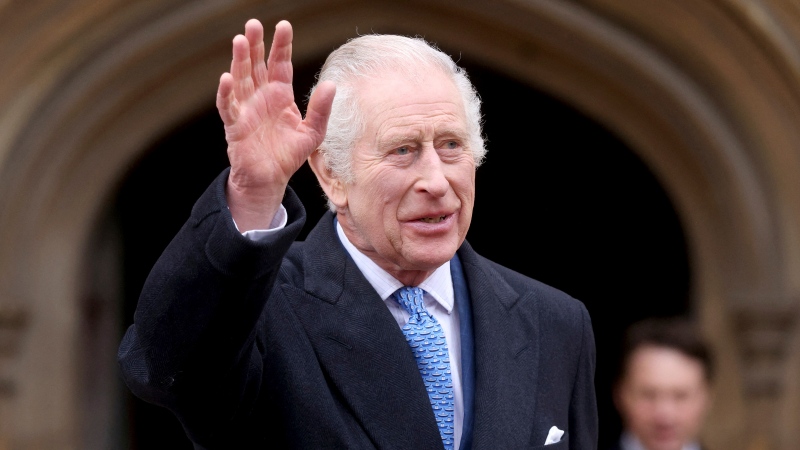

BREAKING King Charles' cancer treatment progressing well, says Buckingham Palace
King Charles III’s doctors are 'sufficiently pleased' with his cancer treatment and he is expected to return to public-facing duties, Buckingham Palace announced on Friday.
BREAKING Orca calf that was trapped in B.C. lagoon for weeks swims free
An orca whale calf that has been stranded in a B.C. lagoon for weeks after her pregnant mother died swam out on her own early Friday morning.
'Unacceptable': Trudeau reacts after AFN chief says headdress taken from plane cabin
After the Assembly of First Nations' national chief said her headdress was taken from an airplane cabin this week, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau called the incident 'unacceptable' and a 'mistake' on the part of Air Canada.
Sophie Gregoire Trudeau on navigating post-political life, co-parenting and freedom
Sophie Gregoire Trudeau says there is 'still so much love' between her and Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, as they navigate their post-separation relationship co-parenting their three children.
From faulty kids' cribs to flammable kids' bathrobes, here are the recalls of the week
Health Canada issued recalls for various items this week, including kids’ bathrobes, cribs and henna cones.
Taylor Swift dons Montreal designer's dress in 'Fortnight' video
A pair of Montreal designers' work has now been viewed over 41 million times. Taylor Swift dons a Victorian throwback black gown in her latest music video, 'Fortnight', designed by UNTTLD due Simon Belanger and Jose Manuel Saint-Jacques.
'Too young to have breast cancer': Rates among young Canadian women rising
Breast cancer rates are rising in Canada among women in their 20s, 30s and 40s, according to research by the University of Ottawa (uOttawa).
'Violation': CSIS had officer investigated after she reported a superior raped her
A CSIS officer's allegations that she was raped repeatedly by a superior in agency vehicles set off a harassment inquiry, but also triggered an investigation into her that concluded the alleged attacks were a “misuse” of agency vehicles by the woman.
'I was scared': Ontario man's car repossessed after missing two repair loan payments
An Ontario man who took out a loan to pay for auto repairs said his car was repossessed after he missed two payments.